Test Methods of Reliability of Valves
According to different valve types and different use positions of marine valves, their stress sources are different. Taking the most widely used globe valves among marine valves as an example, the reliability test design is carried out. In actual use, the main failure modes and failures of the globe valve are the same as those of other valves, which are mainly due to corrosion, leakages and damage to the casing caused by long-term cutting and throttling of the medium. Combined with the operating environment of the marine globe valve, the fatigue durability of the globe valve and the influence of external force on the strength of the valve under a certain medium are confirmed as the key points of the reliability test assessment. Combined with the test standard JB/T 53174-1999, the reliability test is determined. The combination of static pressure life and vibration is adopted.
Table 1 Test conditions of vibration
Table 1 Test conditions of vibration
| Types of vibrations | Transport random vibrations |
| Frequency range (Hz) | 10 to 200 |
| Magnitude (total root mean square value R.M. S, m/ S2) | 10 |
| Single vibration time (min) | 20 |
| Frequency ranges (Hz) | 10 to 200 |
1.1 Vibration tests
The vibration stress applied in the test is shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
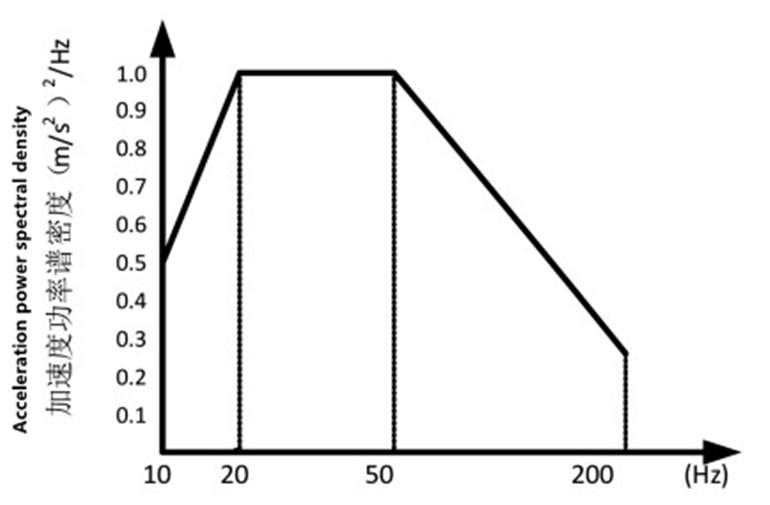
Figure 1 Vibration spectrum
1.2 Static pressure life tests
The static pressure life test is a test of cyclic operation from fully open to fully closed when the globe valve is under the action of medium pressure under laboratory conditions. During the test, the pressure should be 1 to 1.1 times the maximum working pressure of the relevant valve. The maximum working pressure of the valve can refer to the standard or technical requirements of the relevant valve. The test medium is water or gas, which should be according to the actual use medium of the valve. The opening and closing cycle of the valve is carried out at the specified frequency, that is, once per 2 minutes until the standard required number of times is reached.
1.3 Test sections
The test section adopts the combined stress of vibration and static pressure life test. The application method is shown in Figure 2. This section is a 24-h cycle. During the reliability test, a specified number of endurance cycles should be opened and closed according to the valve design requirements. The durability times required by the quality level are different. See Table 2 for details.
Table 2 Numbers of static life tests
| Types of valves | Qualified products | Top-quality goods | High-class products | |
| Iron globe valves | Metal sealing, DN less than and equal to 150mm | - | Greater than and equal to 2000 | Greater than and equal to 6000 |
| Metal sealing, DN greater than and equal to 200mm | - | Greater than and equal to 2500 | Greater than and equal to 4000 | |
| Metal sealing, DN less than and equal to 150mm | - | Greater than and equal to 4000 | Greater than and equal to 6000 | |
| Steel globe valves | Metal sealing, DN greater than and equal to 200mm | - | Greater than and equal to 2500 | Greater than and equal to 4000 |
| Metal sealing, DN less than and equal to 150mm | - | Greater than and equal to 5000 | Greater than and equal to 8000 | |
| Bellows | - | Greater than and equal to 3000 | Greater than and equal to 5000 | |
1.4 Test items
Before the test, under standard atmospheric conditions, check the operating torque of the debugged and installed valve, the leakage of each sealing surface, at the packing and the valve bonnet. During the test, after every 100 operation durability tests, the operating torque of the valve, the leakage of each sealing surface, the leakage at the packing and the valve bonnet shall be checked.
After the specified number of tests are conducted, the operating torque of the valve, the leakage of each sealing surface, the packing and valve bonnet shall be tested under standard atmospheric conditions.
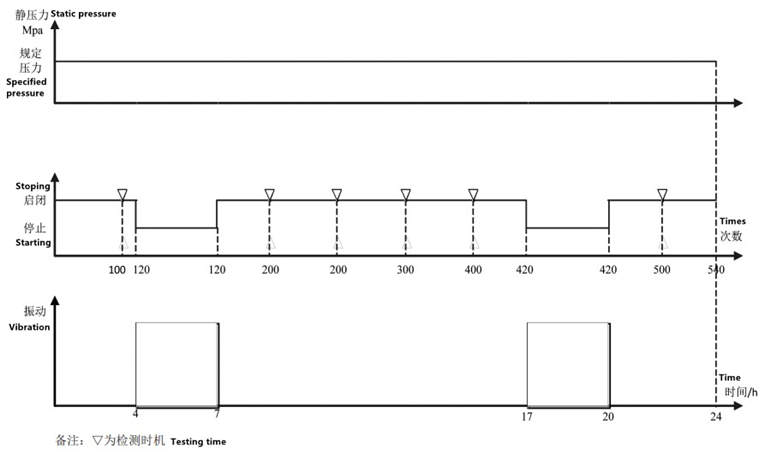
Figure 2 Reliability test sections
2. Conclusion
The reliability test design is conducted in this article by confirming the key stress that causes the valve failure, and provides a fast and effective method for the assessment and verification of the valve reliability level.




