Selection and Design of Dedicated Valves for High Temperature Oil Slurry (Part Two)
4. Special wear-resistant structure of valves
4.1 Valve bodies and wedges
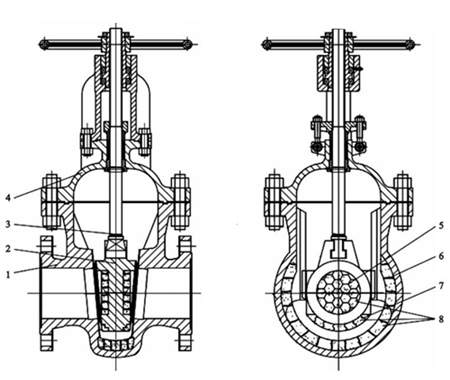
The oil slurry is an incompressible liquid, so a lining structure is designed for the wedge and internal cavity of the high temperature oil slurry valve of a DN less than or equal to 200 (Figure 1). The two end passage of the valve body is not lined and the outer wall of the two end passage of the valve is thickened by 15 to 20mm; the crotch of the valve body is widened. This not only reduces the scouring of catalyst of the high temperature oil slurry to valve bodies, but also facilitates the construction of the lining. As for high-temperature slurry valves whose DN is greater than or equal to 250, the crotch of the valve body is not widened and a lining structure is designed for the wedge, two end passage of the valve body and inner cavities of valve bodies of the high temperature oil slurry valve. Because the high temperature oil slurry is easy to scour the valve, the lining is added in inner cavities of valve bodies and pits in the middle of wedges in the pressure-bearing parts with lining. The parts with the lining are surfacing welded with high-temperature heat-resistant steel, and the height of the welding is up to 30mm. The two sides of the lower end of the wedge are most severely scoured by the catalyst particle medium in the opening and closing process of the valve. The lining is provided for the wedge.
4.1 Valve bodies and wedges
The oil slurry is an incompressible liquid, so a lining structure is designed for the wedge and internal cavity of the high temperature oil slurry valve of a DN less than or equal to 200 (Figure 1). The two end passage of the valve body is not lined and the outer wall of the two end passage of the valve is thickened by 15 to 20mm; the crotch of the valve body is widened. This not only reduces the scouring of catalyst of the high temperature oil slurry to valve bodies, but also facilitates the construction of the lining. As for high-temperature slurry valves whose DN is greater than or equal to 250, the crotch of the valve body is not widened and a lining structure is designed for the wedge, two end passage of the valve body and inner cavities of valve bodies of the high temperature oil slurry valve. Because the high temperature oil slurry is easy to scour the valve, the lining is added in inner cavities of valve bodies and pits in the middle of wedges in the pressure-bearing parts with lining. The parts with the lining are surfacing welded with high-temperature heat-resistant steel, and the height of the welding is up to 30mm. The two sides of the lower end of the wedge are most severely scoured by the catalyst particle medium in the opening and closing process of the valve. The lining is provided for the wedge.

1. Valve bodies 2. Wedges 3. Valve stems 4. Valve bonnets 5. Tortoiseshell nets 6. Insulation nails 7. S-shaped stainless steel reinforcement sheets 8. linings
Figure 1 Dedicated valves for the high temperature oil slurry
Figure 1 Dedicated valves for the high temperature oil slurry
4.2 Sealing surfaces of valves
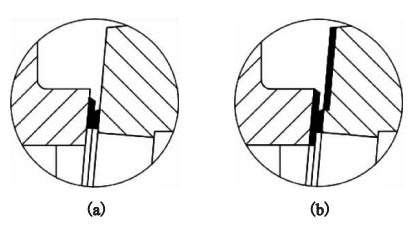
(a) General products (b) Dedicated valves for the high temperature oil slurry
Figure 2 Structure of sealing surfaces
Cobalt-based cemented carbide is surfacing welded on entire surfaces of valve seats of valve bodies' two sides and sealing surfaces of wedges (Figure 2), and maximum width of the cobalt-based cemented carbide on the sealing surface of the wedge should be ensured. The surfacing thickness of the sealing surface of the high-quality alloy is greater than or equal to 2mm.
5. Use and maintenance of the valve's lining
The lining material for inner cavities of valves and wedges for the high temperature oil slurry is very important to ensure the service life of the valve. Adopting a special lining structure and method, effectively overcomes the disadvantages of poor firmness and unreliable sealing of general linings and accidents caused by lining falling and damaging the slurry pump bodies (Figure 3). Therefore, the use of the lining should be in accordance with the requirements and the maintenance of the valve's lining.

Figure 3 Dedicate valves for the high temperature oil slurry of petrochemical catalysis units (painted in orange)
5.1 Construction
(1) Check the shelf life of the lining's material TA-218 to ensure that it is used within the shelf life.
(2) It is advisable to evenly mix the TA-218 and the adhesive. The mixed materials should be used up as soon as possible. The materials that have been hardened should not be mixed with water again.
(3) Fill the frame with mixed materials twice. After filling, use a mallet or rubber hammer to tamp and make the material evenly covered
5.2 Linings
(1) Valves that are lined should be placed in an idle place, and they shouldn't be moved or collided.
(2) Keep them for 24 hours in dry and circulated air, and they should not be in contact with water.
(3) Inspect and repair them.
(4) After they were kept for 24 hours, use a small hammer to lightly tap valves every 100mm. The sound should be low.
(5) If there is any cavity or looseness, the loose parts should be removed and repaired in time.
(6) The repaired valve should be kept for another 24 hours.
(7) The well maintained valve should be placed in a resistance furnace for ceramic solidification, heating and baking (Table 2).
Table 2 Ceramic solidification after heating lining materials
| Temperature ranges/℃ Room temperature to 315℃ |
Heating rates/(℃/h) Less than or equal to 30 |
Time/h From 10 to 12 |
| 315℃ | Constant temperature | 2 |
| From 315℃ to 540℃ | Less than or equal to 30 | From 7 to 8 |
| 540℃ | Constant temperature | 2 |
| From constant temperature to 540℃ | Air cooling |
6. Testing methods
The shell strength test of the dedicated valve for the high temperature oil slurry is in accordance with the regulations of GB/T26480 and must be carried out before adding the valve's lining. After the valve is lined, only a low-pressure air tightness test is performed. The testing media should be dry and clean air, nitrogen, or other inert gases.
7. Conclusion
High temperature oil slurry dedicated valve series products are mainly used in petroleum refining equipment where the media are high temperature oil slurry and similar media to prevent the medium from scouring the shell and prolong the service life. The internal cavity of valve bodies and wedges of the high temperature oil slurry valve adopts a special lining structure and method, which overcomes the shortcomings of poor firmness and unreliable sealing of general valves with linings and the accidents caused by lining falling off and damaging the oil slurry pump body. The service life of high temperature slurry valves in many Chinese large-scale petrochemical heavy-duty devices is 10 times longer than that of ordinary gate valves, which eliminates the hazard of fire safety in refineries in particular, improves the working environment, and creates economic and social benefits.




