NDT for Inspecting Performance and Quality of Valves
- Oct Sat, 2021
- Hits: 180

In the casting process of a valve, sometimes there are defects such as gas holes, porosity, impurities, etc., which affect the normal use of the castings. Welding repairs are usually performed. After...
The Design of Valves Is Related to the Costs of Valves
- Sep Sun, 2021
- Hits: 22

Reducing costs are the goals of various industries and the valve industry is no exception. Some owners in the valve industry think that the design cost of valves greatly influences the overall cost...
The Structure Design of LNG Ultra-low Temperature Valves
- Jul Wed, 2021
- Hits: 84

1. The longneck bonnet structure The temperature of LNG is -162°C, which is extremely low. The working temperature of the packing of the valve should not be lower...
LNG Cryogenic Valves
- Jul Mon, 2021
- Hits: 50

1. Liquefied natural gas With the development of industry and the improvement of people's living standards, natural gas, especially liquefied natural gas has become the most indispensable high-quality...
The Analysis of Breaking of Screws of the Natural Gas Gate Valve's Flange
- Jun Wed, 2021
- Hits: 16

When a natural gas company was inspecting and repairing the pipeline, it was found that some of the fastening screws of flanges of gate valves were broken. The gate valve is buried below ground. The...
Sixteen Common Questions in Selection of Valves (Part Two)
- Jun Wed, 2021
- Hits: 9

11. Why is the anti-blocking performance of control valves with straight strokes poor, while that of the rotary motion valve is good? Valve spools of straight strokes throttle vertically, and the medium...
Sixteen Common Questions in Selection of Valves (Part One)
- May Fri, 2021
- Hits: 19

A valve is one of the indispensable devices in industrial production, and you may encounter many questions from selection, use to the maintenance of valves. Some common questions are listed in this article....
Advantages and Disadvantages of Soft Sealing Gate Valves
- May Wed, 2021
- Hits: 39

Overview of soft sealing gate valves A soft sealing gate valve is a manual valve used to connect media in water conservancy projects. A soft seal gate valve is composed of valve seats, valve bonnets,...
Selection and Design of Dedicated Valves for High Temperature Oil Slurry (Part Two)
- Apr Thu, 2021
- Hits: 14
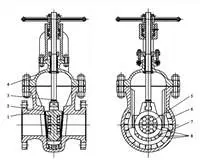
4. Special wear-resistant structure of valves 4.1 Valve bodies and wedges The oil slurry is an incompressible liquid, so a lining structure is designed for the wedge and...
Selection and Design of Dedicated Valves for High Temperature Oil Slurry (Part One)
- Apr Fri, 2021
- Hits: 23
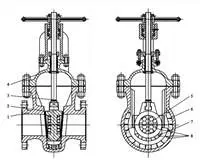
Abstract: The harsh working conditions of high temperature oil slurry with catalyst particles and media containing hydrogen sulfide are introduced; the selection principles of dedicated...
The core technologies of safety valves
- Mar Mon, 2020
- Hits: 28

A safety valve is an automatic valve that does not use any external force and uses the force of the medium to discharge a rated amount of fluid to prevent the pressure from exceeding the rated safe value....
Pressure Tests for Ball Valves, Butterfly Valves and Other Industrial Valves
- Oct Fri, 2019
- Hits: 31

01. Pressure test methods for ball valves The strength test of the pneumatic ball valve should be carried out with the ball half open. ① Floating ball valve tightness test: the valve is in a half-open...
Pressure Tests for Gate Valves, Throttle Valves, and Globe Valves
- Oct Fri, 2019
- Hits: 30

In general, industrial valves are not tested for strength during use, but the valve body and bonnet after repair or corroded body and bonnet should be tested for strength. For safety valves, the constant...
Requirements for valves installed on the underground piplines
- Sep Tue, 2019
- Hits: 24

With the strengthening of China's environmental awareness and the change of energy structure, China's urban gas industry has made a great progress. The fuel gas types have evolved from simple...
The forms of the metal valve corrosion and their prevention methods
- Jun Fri, 2019
- Hits: 26

Corrosion is the destruction and deterioration of materials under various environmental conditions. Metallic corrosion is mainly caused by chemical corrosion and electrochemical corrosion. Non-metallic...
Technical characteristics of all welded ball valves and its split valve body
- Apr Mon, 2019
- Hits: 129

Design method of the split valve body of all-welded ball valves: The valve body design of the all-welded ball valve has a cylindrical structure and a spherical structure, and the cylindrical structure...
Pressure adjustment and operating procedures for safety valves
- Apr Wed, 2019
- Hits: 134

1. The adjustment of opening pressure 1.1 Before the safety valve is delivered from the factory, the opening pressure should be adjusted one by one to the user's required setting value. If the user...
Acoustic online detection of valve internal leakage
- Mar Thu, 2019
- Hits: 151

The pressure-bearing valves of ground facilities and equipment in an oil field have experienced internal leakage due to wear, corrosion or other reasons. Because the internal leakage is difficult to find,...
How to ensure a gas-tight seal of a valve after a long time of use?
- Mar Tue, 2019
- Hits: 61

After a valve is used for a long time, the sealing surface of the valve disc and the valve seat will wear and the tightness will be affected. Repairing the sealing surface is a large and important task....
The working principle of self-operated regulating valves
- Feb Tue, 2019
- Hits: 335

A self-operated regulating valve is also called a self-operated control valve. It is a new type of regulating valve. As the name implies, it does not need external power supply and secondary instrument....



